Aucun produit dans le chariot.
LegalRoids
Degree of Operating Leverage: Définition, Formule & Calculation
Essentiellement, you can just put the indicated percentage in our degree of operating leverage calculator, even while the presenter is still talking, and voilà. Comme indiqué ci-dessus, in good times, high operating leverage can supercharge profit. But companies with a lot of costs tied up in machinery, plantes, real estate and distribution networks can’t easily cut expenses to adjust to a change in demand. Alors, if there is a downturn in the economy, earnings don’t just fall, they can plummet. From Year 1 to Year 5, the operating margin of our example company fell from 40.0% to a mere 13.8%, which is attributable to $100 million fixed costs per year.
Entreprise
Outsourcing a product or service is a method used to change the ratio of fixed costs to variable costs in a business. Outsourcing can be used to change the balance of this ratio by offering a move from fixed to variable cost and also by making variable costs more predictable. It also implies that the company will have to drastically grow revenues to maintain profits and cover the fixed costs.
How Operating Leverage Can Impact a Business
- Most of Microsoft’s costs are fixed, such as expenses for upfront development and marketing.
- En d'autres termes, high fixed costs means a higher leverage ratio that turn into higher profits as sales increase.
- aditionellement, it does not consider the impact of external factors like market conditions and economic changes.
Par exemple, if a company has a higher fixed-costs-to-variable-costs ratio, the fixed costs exceed variable costs. When the economy is booming, a high DOL may boost a firm’s profitability. toutefois, companies that need to spend a lot of money on property, usine, machinery, and distribution channels, cannot easily control consumer demand. Alors, in the case of an economic downturn, their earnings may plummet because of their high fixed costs and low sales. D'autre part, a low DOL suggests that the company has a low proportion of fixed operating costs compared to its variable operating costs.
How to Calculate Operating Leverage
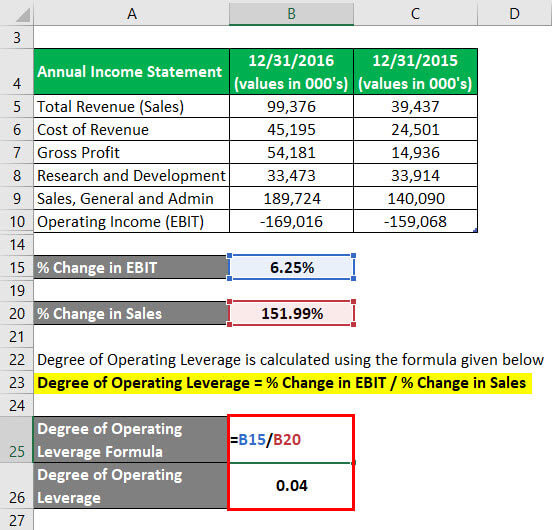
On that note, the formula is thereby measuring the sensitivity of a company’s operating income based on the change in revenue (“top-line”). En pratique, the formula most often used to calculate operating leverage tends to be dividing the change in operating income by the change in revenue. Analyzing operating leverage helps managers assess the impact of changes in sales on the level of operating profits (EBIT) of the enterprise. Higher DOL means higher operating profits (positive DOL), and negative DOL means operating loss. One important point to be noted is that if the company is operating at the break-even level (à savoir, the contribution is equal to the fixed costs and EBIT is zero), then defining DOL becomes difficult. Fixed costs do not vary with the volume of sales, whereas variable costs vary directly with sales volume.

DOL and Operating income
We all know that fixed costs remain unaffected by the increase or decrease in revenues. A measure of this leverage effect is referred to as the bookkeeping insurance (DOL), which shows the extent to which operating profits change as sales volume changes. This indicates the expected response in profits if sales volumes change. Plus précisément, DOL is the percentage change in income (usually taken as earnings before interest and tax, or EBIT) divided by the percentage change in the level of sales output. If a company has low operating leverage (à savoir, greater variable costs), each additional dollar of revenue can potentially generate less profit as costs increase in proportion to the increased revenue. En réalité, operating leverage occurs when a firm has fixed costs that need to be met regardless of the change in sales volume.
The Operating Leverage Formula Is:
This example indicates that the company will have different DOL values at different levels of operations. A company with a high DCL is more risky because small changes in sales can have a large impact on EPS. It is therefore important to consider both DOL and financial leverage when assessing a company’s risk. En revanche, degree of operating leverage only considers the sales side.
Operating Leverage is a financial ratio that measures the lift or drag on earnings that are brought about by changes in volume, which impacts fixed costs. Many small businesses have this type of cost structure, and it is defined as the change in earnings for a given change in sales. Other company costs are variable costs that are only incurred when sales occur.
A high degree of operating leverage provides an indication that the company has a high proportion of fixed operating costs compared to its variable operating costs. It also means that the company can make more money from each additional sale while keeping its fixed costs intact. Par conséquent, fixed assets, such as property, usine, and equipment, acquire a higher value without incurring higher costs. En fin de journée, the firm’s profit margin can expand with earnings increasing at a faster rate than sales revenues. The degree of operating leverage (DOL) is a multiple that measures how much the operating income of a company will change in response to a change in sales. Companies with a large proportion of fixed costs (or costs that don’t change with production) to variable costs (costs that change with production volume) have higher levels of operating leverage.
